Drupal 8 empowers Drupal powered websites with global reach. The admin interface includes built-in translation. Users can translate everything in the system using built-in user interfaces. Also, we can create pages containing views language filtering as well as block visibility. One is able to obtain translation updates automatically from the vast Drupal community.
Drupal 8’s Configuration Translation enables the translation of essential elements—blocks, toolbars, menus, etc.
- The Content Translation module can address our website’s copywriting, like articles et al.
- The Interface Translation module enables the other page elements (e.g. form labels) to be translated.
- The Language module allows us to define which languages our website supports.
With these essential features, Drupal 8 positions itself as the global ready website option. Multilingual feats like translation and transliteration are two pillars of this positioning.
Translation
Drupal 7 has regional settings, language support, and usability attention given to interface translation, however Drupal 8 brings this into the core. It comes with highly improved language detection abilities that are browser based, meaning it functions to identify preferred languages and present them to users automatically.
There are 94 languages and counting, one of which that we can assign as a website default for content and configurations. Blocks can also be language dependent. Further, more page elements than ever are now Blocks in Drupal 8, granting greater translation accessibility.
Transliteration
There are times when characters need to be romanized for various purposes. Drupal core has addressed this. Now, built-in user interfaces transliterate key language assignments. This transliteration is an advancement from other CMS solutions, enabling efficient romanization of several challenging scripts and types (e.g. Hungarian, Czech, Marathi)
Here are the basic steps involved in building Drupal 8 Multi-lingual site.
Step-1:
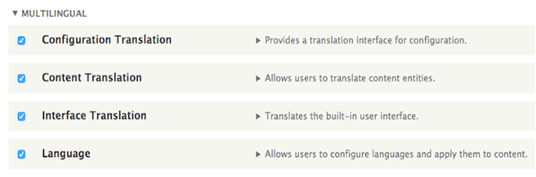
Enable the translation modules – need to enable these following four core Drupal modules in order to translate our site.
Step-2:
Translate the Drupal core
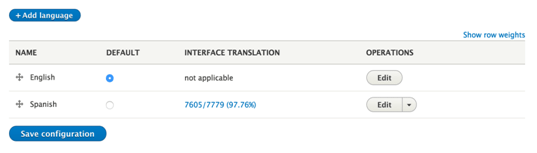
- a. Go to Configuration > Languages. Click “Add language”

- Choose your language and click “Add language”.

- Click on the percentage area, under “Interface Translation”.
 We will be able to search for and manually translate all the language strings in here:
We will be able to search for and manually translate all the language strings in here:

Step-3:
Translate our own site setup
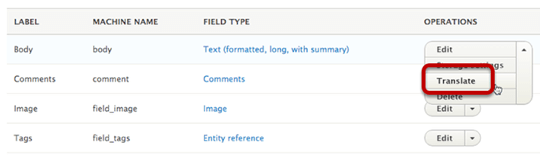
- Go to Structure > Content types, we’ll see a “Translate” option for our content types:
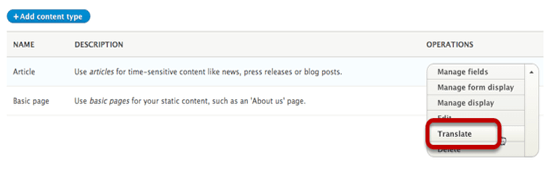 Inside the next screen, we’ll see similar “Translate” links for all fields:
Inside the next screen, we’ll see similar “Translate” links for all fields:
Step-4:
Add Content : can add content to our Drupal site.
- Go to Configuration > Content language and translation. Click the box next to “Content”.
- Check the box, “Show language selector on create and edit pages”- this helps us to choose the language. Content can be added to the site.
- After saving content, we’ll see a “Translate” tab available:
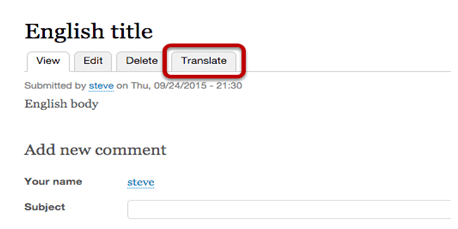 Click “Add” in order to create a new version of that content item:
Click “Add” in order to create a new version of that content item:

Step-5:
Allow users to switch between languages.
- Go to Structure > Blocks. Click “Place blocks”.
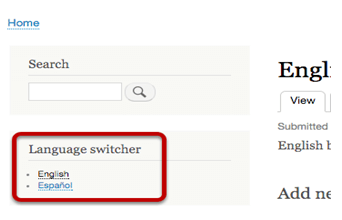
- Click “Place block” next to the “Language Switcher” block:

- Click “Save block”.
- If we observe in the site front, the Language Switcher will be working
 With these details, this blog covers how Drupal 8’s multilingual system works and also the core features and API’s in Drupal 8 for multilingual needs.
With these details, this blog covers how Drupal 8’s multilingual system works and also the core features and API’s in Drupal 8 for multilingual needs.