As a business owner, you don’t suddenly decide it’s time for ERP automation. It becomes noticeable when everyday operations start demanding more energy than they should. Simple processes need follow-ups, data sits in too many places, and decisions slow down because clarity is missing. Over time, that extra effort adds up and ERP automation becomes less of an option and more of a necessity.
How ERP Automation Works
ERP automation empowers businesses to harness the full potential of their ERP systems, making operations more efficient, cost-effective, and responsive to changing market demands.
Here’s how it works:
Identifying Repetitive Tasks
The first step in ERP automation is to identify repetitive and rule-based tasks within the organization’s business processes. These tasks can range from data entry and document processing to inventory management and reporting.
Defining Automation Rules
Once identified, automation rules or workflows are created. These rules specify the conditions under which certain actions should occur automatically. For example, an automation rule could dictate that a purchase order is automatically generated when inventory falls below a certain level.
Integration with ERP System
Automation tools or software are integrated with the ERP system. This integration allows the automation tools to access data and perform actions within the ERP system based on the defined rules.
Data Collection and Processing
Automation tools collect data from various sources, including sensors, databases, and external systems. This data is then processed according to the predefined rules. For instance, data from sales transactions can be automatically recorded in the ERP system, eliminating the need for manual data entry.
Decision-Making
Automation systems can be programmed to make better business decisions based on data and rules. For example, an ERP automation system can analyze sales trends and automatically adjust inventory levels or reorder products when needed.
Notification and Reporting
ERP automation can trigger notifications and generate reports. For instance, if a payment is received, the system can automatically update the financial records and send a notification to the relevant department.
Error Handling
Automation systems are designed to handle exceptions and errors. If a rule cannot be executed due to an issue or inconsistency, the system can trigger alerts for human intervention.
Continuous Improvement
ERP automation is not a static process. It can be refined and improved over time as business processes evolve. Regular monitoring and analysis of automated processes help identify opportunities for optimization.
Scalability
ERP automation can scale to accommodate growing business needs. The automation system can handle increased data volumes and more complex workflows as the organization expands.
Security and Compliance
Security measures are put in place to ensure that sensitive data is protected. Compliance with regulations and standards is also crucial in ERP automation to avoid legal issues.
Related reads: ERP Integration Challenges Explained [+10 Solutions]
Best Practices of Automating Your ERP
Here are some key points to take care of:
1. Start with the pain
The best ERP automation projects begin with frustration. Late orders, inventory mismatches, manual reconciliations, those are your signals. Automate the processes that slow people down every day, not the ones that just look impressive on a demo.
2. Fix the process before you automate it
Automation doesn’t fix broken workflows, it scales them. If approvals are unclear or data ownership is messed up, automating that process will only make the confusion faster. Take time to simplify and standardize how work gets done before layering automation on top.
3. Don’t try to automate everything at once
This is where many projects struggle. The smarter approach is incremental — order processing first, then inventory, then finance, and so on. Early wins build confidence, adoption, and internal buy-in, which matter more than going live with everything on day one.
4. Keep data clean and consistent
ERP automation is only as good as the data behind it. Make sure item masters, customer records, pricing, and vendor data follow clear rules. Clean data reduces errors, improves reporting, and prevents teams from losing trust in the system.
5. Involve the people who actually use the system
The best insights rarely come from leadership alone. Warehouse teams, customer service reps, planners, and finance users know where manual work really happens. Involving them early makes automation more practical and improves adoption later.
6. Integrate, don’t isolate
ERP automation works best when systems talk to each other, be it CRM, WMS, eCommerce, EDI, shipping, or accounting. Avoid building silos inside the ERP itself. Integration ensures information flows end-to-end, without manual handoffs.
7. Measure what actually improved
After automation, look at tangible outcomes: fewer errors, faster order cycles, shorter close periods, better inventory turns. These signals confirm whether automation is doing its job or if something needs adjustment.
Also read: The Definitive Guide on ERP Integration with Salesforce
Benefits of ERP Automation
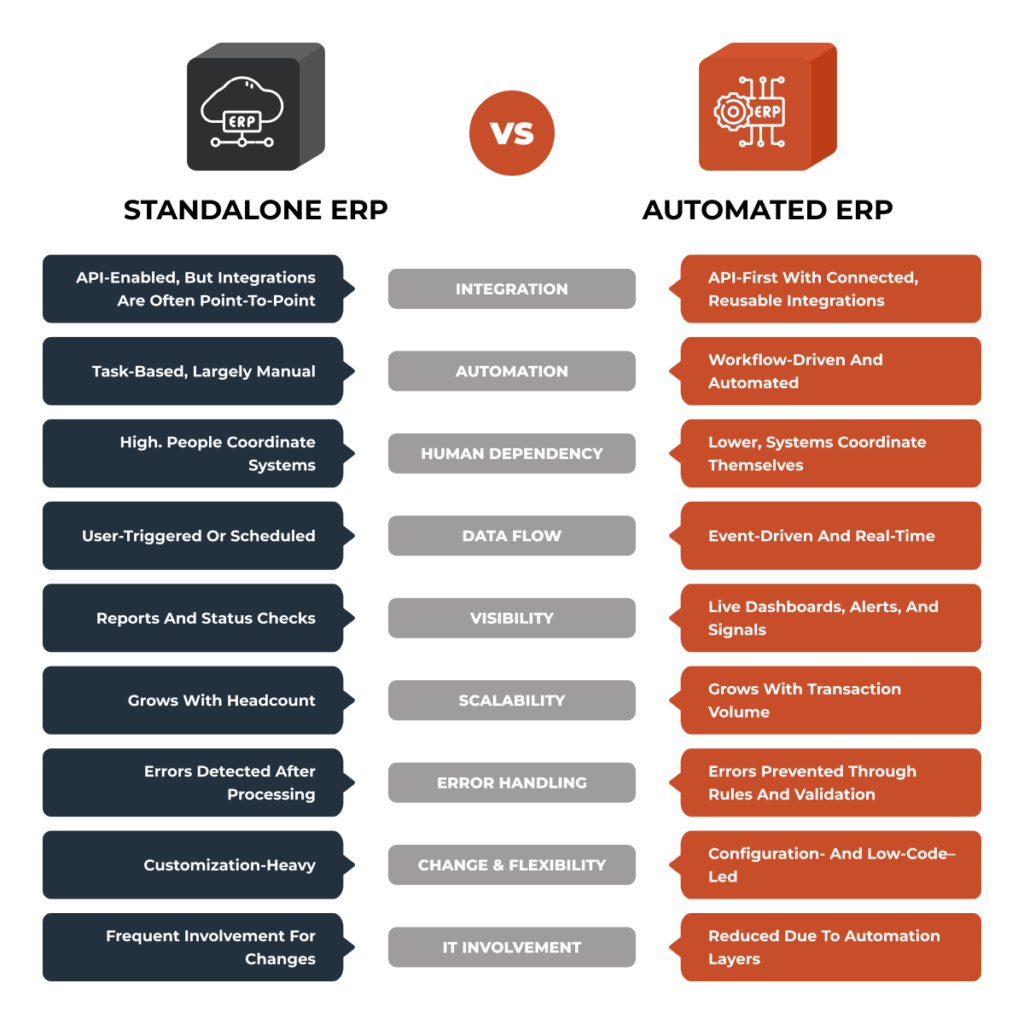
ERP automation offers several benefits, let’s break them down below.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
ERP automation streamlines repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on more strategic and value-added activities.
This boosts overall efficiency and productivity within the organization. For example, data entry and document processing are time-consuming tasks, and automating them will reduce the time employees spend on these routine tasks, enabling them to dedicate their efforts to more critical responsibilities.
Enhanced Data Accuracy and Reduced Errors
Automation minimizes the risk of human errors that can occur during manual data entry and processing. ERP automation systems ensure that data is consistently accurate and up to date. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity of financial records, inventory levels, and other critical business information.
Cost Savings Through Reduced Manual Effort
Organizations can achieve cost savings by automating tasks that would otherwise require significant human effort. Reduced operational costs, fewer errors, and increased efficiency contribute to these savings. For instance, automating invoice processing can eliminate the need for dedicated accounts payable staff to handle each invoice manually.
Real-time Data Insights for Decision-making
ERP automation provides real-time data insights, allowing decision-makers to access up-to-the-minute information about the state of the business. This facilitates quicker and more informed decision-making. For example, sales trends, inventory levels, and financial metrics can be continuously updated and readily available for analysis.
Scalability and Adaptability for Growing Businesses
ERP automation systems are scalable and adaptable to accommodate the changing needs of growing businesses. As organizations expand, the automation system can handle increased data volumes, more complex workflows, and additional integrations with other systems. This scalability ensures that the automation remains effective as the business evolves.
These ERP benefits streamlines processes and improves business functions by reducing manual workloads. In addition, it significantly contributes to enhancing business operations and gaining a competitive edge in the market.
Related reads: ERP In Supply Chain Management: A Distributor’s Guide
Common ERP Processes to Automate
When you think of automating your ERP, the key is to not automate everything at once. Pick some of the most redundant processes and start automating them. Here are some of the common ones to start with:
1. Order Processing and Fulfillment
This is often the first breaking point. Orders come in through sales reps, EDI, emails, or ecommerce portals, and someone has to manually enter them into the system, causing delays and errors. But when you automate, it ensures orders flow directly into ERP, inventory updates immediately, and fulfillment teams work with accurate information without constant back-and-forth.
2. Inventory Management and Replenishment
Inventory issues don’t always show up as big problems at first. They show up as small issues like stockouts, excess inventory, or mismatched numbers across locations. ERP automation gives real-time visibility into inventory across warehouses and helps trigger replenishment at the right time, based on actual demand instead of assumptions.
3. Procurement and Supplier Coordination
Buying materials or products shouldn’t depend on email threads and manual follow-ups. With ERP automation, purchase orders, approvals, and supplier updates follow a defined flow. This helps teams avoid last-minute purchasing, maintain better vendor relationships, and keep production or distribution schedules steady.
4. Billing, Invoicing, and Financial Reconciliation
Finance teams often feel the pain of manual processes the most. Matching invoices to purchase orders and receipts takes time and invites errors. ERP automation streamlines invoicing and reconciliation, shortens month-end close, and keeps financial data consistent and reliable across the business.
5. Production Planning and Scheduling
For manufacturers, production plans change more often than expected due to demand shifts, material availability, or capacity constraints. ERP automation helps adjust schedules based on real-time data, reducing downtime, bottlenecks, and guesswork on the shop floor.
6. Reporting and Operational Visibility
Many businesses don’t realize how much time they spend just trying to see what’s happening. Automation in this case, brings sales, inventory, operations, and financial data into one view. Instead of chasing updates, leaders can make decisions based on current, accurate information
Why DCKAP Integrator Is a Strong Choice for ERP Automation
If you’re serious about ERP automation, the platform you choose matters just as much as the ERP itself.
One tool you can absolutely rely on, in this case, is DCKAP Integrator. It’s designed specifically around the way manufacturers and distributors actually use ERPs. Over the years, it has worked closely with most of the ERPs common in this space, including Epicor (Prophet 21, Eclipse, Kinetic, Bistrack), Infor (SX.e, M3), Sage (X3, 100, 300), Acumatica, NetSuite, Microsoft Dynamics, and more.
Here’s why many businesses choose DCKAP Integrator:
Deep ERP understanding with an ERP-first approach
DCKAP Integrator is designed to keep the ERP as the central source of truth. All other systems in your tech stack like eCommerce, CRM, WMS, EDI, shipping tools, connect to the ERP. This keeps data consistent, reliable, and aligned with how the business actually runs.
End-to-end ERP automation
This isn’t just about connecting systems. DCKAP Integrator supports end-to-end automation across key business processes from order intake to fulfillment, inventory updates, invoicing, and beyond, so automation actually carries through the entire operation.
Backed by real expertise
Behind the platform is a dedicated team that works with different ERPs every day. This experience matters. It means integrations are built with an understanding of ERP nuances, edge cases, and real-world scenarios, so you’re not learning lessons the hard way.
Best for complex, high-volume operations
No two businesses run the same way. DCKAP Integrator handles complex logic, large transaction volumes, and custom requirements with ease. The team can design custom workflows and integrations that match how you operate, so you don’t have to adjust your processes to fit the system.
Flexible enough to grow and change
Businesses evolve. Systems get added, replaced, or upgraded. DCKAP Integrator is built to adapt to those changes without disrupting existing workflows or forcing you to rebuild integrations from scratch.
Strong support and ongoing maintenance
ERP automation doesn’t end at go-live. Ongoing support, monitoring, and maintenance ensure integrations continue to work as the business grows and changes, without becoming another system teams have to worry about.
Transparent pricing
One thing many businesses appreciate is the clarity around pricing. DCKAP Integrator offers transparent pricing with plans that work for different business sizes and needs. You can explore the pricing details and see how it’s structured for yourself by checking out the pricing page here.
If you’re looking for ERP automation that’s clear, flexible, and built around how your business actually works, DCKAP Integrator is worth a closer look. The best way to understand how it fits into your operations is to see it in action. Check out a live demo and explore how ERP-first automation can work for you.
FAQs
What is an automated ERP system?
An automated ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system refers to the integration of automation technology within an ERP platform. It involves using software tools to streamline and optimize entire processes, reducing manual effort and improving efficiency.
What are some best practices for implementing ERP automation?
Best practices include thorough planning, clear objectives, employee training, and continuous monitoring. It’s also important to choose automation solutions that align with your business goals.
How does ERP automation contribute to a central database?
ERP automation ensures that data from various departments and functions is collected, processed, and stored in a centralized database. This centralization enhances data consistency and accessibility.
Why is having a single platform for ERP automation advantageous?
A single platform simplifies management, reduces integration challenges, and promotes seamless communication between different parts of the organization. It also allows for better data sharing and reporting.
How does ERP automation lead to better service for customers?
ERP automation can improve response times, order processing, and customer support. It ensures that accurate and up-to-date information is readily available, enhancing the overall customer experience.
Is ERP automation suitable for all types of businesses, regardless of their size?
ERP automation can benefit businesses of all sizes. It can scale to accommodate the needs of small businesses and large enterprises, making it adaptable and beneficial for a wide range of organizations.
What are ERP applications?
ERP applications are software solutions designed to manage and integrate various business processes within an organization. These processes can include accounting, human resources, inventory management, supply chain, customer relationship management (CRM), and more. ERP applications provide a unified platform for data management and decision-making across different departments.
What is robotic process automation (RPA) in the context of ERP automation?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that uses software robots or “bots” to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks within an ERP system. These bots can mimic human actions, such as data entry and data retrieval, to perform tasks with speed and accuracy.
What is Business Process Automation (BPA)?
Business Process Automation is the use of technology to automate, streamline, and optimize routine and repetitive tasks and workflows within an organization. It aims to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and free up employees’ time for more valuable tasks. It is not to be confused with Business Process Analysis.
Is BPA the same as Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
No, BPA is a broader concept that encompasses various technologies, including RPA. RPA focuses specifically on using software robots to automate tasks that mimic human actions, while BPA may involve a wider range of automation methods.