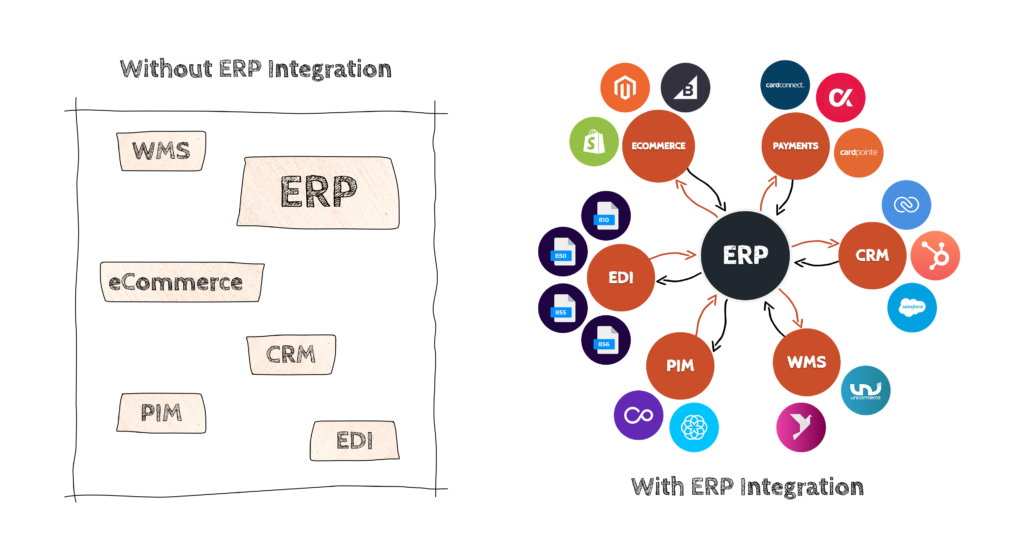
At the heart of most organizations, the Enterprise Resource Planning or ERP system helps simplify the way organizations elicit, track, manage and work with their data across multiple operational teams. But as a company’s tech stack grows, and various teams have specialized tools they use daily, there is an increased risk for outdated information, and increased wasteful manual effort. That’s where ERP integration comes in.
What is ERP Integration?
ERP Integration is connecting and synchronizing your ERP software with other business applications such as eCommerce (front-end), CRM (Customer Relationship Management), EDI (Electronic Data Interchange), PIM (Product Information Management), marketing tools such as analytics, and other databases and data points that your business operates with.
It allows different systems to communicate seamlessly, enabling companies to manage data more efficiently across business functions, from human resource management to customer records.
Why Organizations Opt For ERP Integration
By now, you will have understood what an ERP Integration is in detail, why you need it, and the different types of ERP Integration that can be beneficial for your business.
Automated Business Processes
Since we discussed that customer details, order details, financial information, and other key business-related information arises from many applications and points such as eCommerce, CRM, EDT, EAM. Clearly, it is important that your ERP software gets all this data, as and when it arises.
This can happen only by integrating your ERP with your other business applications. Otherwise, you have to break your heads by manually making the data entries into the ERP, which wastes your productive time. Introducing automation to your business processes can help you to streamline activities and workflows across departments: especially through integration.
Single Source of Truth
Integrating ERP systems with other applications ensures that data from different applications, such as eCommerce and CRM, remain updated in the ERP software.
People from all departments would have data access from a single platform at all stages of the order-to-fulfillment process and then some. For Instance, the inventory management team would have access to the real-time inventory of products available in eCommerce, and can immediately act upon a shortage of products.
The accounts team would not have to wait for the marketing and sales teams for revenue details. Moreover, having all data in the ERP solution ensures that it remains the single source of truth for data and employees refer to data in ERP in case of any discrepancies.
Accuracy of Operations
We now already know ERP Integration automates business processes and provides in-depth analysis of your business processes to reduce the human workload of manual data entry, and it also provides the advantage of a reduction in human error. The accuracy of data in ERP software increases as a result of teams working with the right data.
For instance, without ERP integration, the operations team would have to manually make entry of customer orders from eCommerce, which is error-prone, ultimately leading to the wrong products being delivered and/or sales personnel approaching leads with incorrect requirements.
Improved Efficiency of Time Spent
You are eliminating one of the major time-consuming parts of the work, which is manually entering data into the ERP. This frees you of redundant, burdening work and allows you to spend the equivalent time in other useful business operations, such as market penetration, new feature implementation, business expansion, process optimization, and so on. Better visibility into operations can help across the board, allowing leaders to optimize business processes for the best.
Since ERP System Integration makes accurate real-time data available in the system, you can easily make use of the data to derive high-level actionable insights and make decisions that help take your business to the next level.
Enhanced Workflows
Integrating your ERP with your primary business tools, such as project management, enables the centralization of work-related data. This means everyone in the company will be able to see what others are working on, and you can set priority levels to employee tasks and schedule processes.
Also, knowing what teams are working on will not only help you understand whether the on-going activities are aligned with business objectives, but also make modifications in tasks wherever and whenever necessary.
For instance, if you had asked for a project report from your employee but see that they are working on a priority development task in a project, you can then reschedule the task you assigned accordingly.
Accelerated Sales Conversions
Accelerated conversions in sales mean more website visitors are getting converted into leads and more leads are getting converted into customers in shorter time spans, compared to what it was before integrating your ERP application.
Lead information from CRM and eCommerce immediately flows into eCommerce, which enables all departments to collaboratively work towards specific customer demands and needs. More and more leads are processed effectively in less time, which provides a dual advantage of increased customer satisfaction as well as business revenue. From pre-sales to post, integration can help your teams deliver exceptional customer experiences.
Happier Customers (That Come Back For More)
B2B customers today are expecting near-B2C experiences. And whether consciously or otherwise, they are impacted by any friction in the order-to-fulfillment process. Integration can ensure the enjoy a better shopping experience even before purchase, and are able to gain timely resolutions to any queries or concerns.
Syncing your ERP with tools like the CRM or inventory management tool can help ensure you are best equipped to handle customer needs at every stage. And, in turn, see more returning buyers.
Common Methods Businesses Use To Integrate Their ERP
1. Integration Using APIs
Many software solution providers offer APIs (application program interfaces) for integration. In some cases, even the developers or IT teams can build their own APIs for integration and streamlining the communication between your ERP and other tools that help with a company’s essential business functions. However, this approach is technically complicated as well as resource and time-consuming.
2. Connectors From System Vendors
Some ERP vendors provide their own connectors to sync applications. They can be great, especially when linking from point-to-point, or between two specific solutions that are well-established. However, these solutions are inflexible and only include common use cases, leaving little or no room for customization.
3. Third-Party Integration Solutions
Some vendors specialize in third-party software to help establish those seamless integrations. iPaaS also known as a central platform is a cloud-based, cost-effective, and flexible solution that can connect their ERP and other systems without much hassle. Its cloud technology provides data security, flexibility, and scalability to businesses, even if you intend to add and sync more applications in the future.
iPaaS such as DCKAP Integrator can help ensure better ROI than other methods due to its high-level customization capabilities and scalable architecture. In addition, it is low-code, offers ease of use, and has pre-built templates for effective and seamless connectivity. Different vendors have their own pros and cons, so it’s best to find one that matches your needs.
Also see: ERP Middleware: All You Need To Know [+FAQs]
Top Systems To Connect With Your ERP
There are numerous kinds of SaaS apps that can be integrated with ERP. For best results, ERP System integration is definitely recommended for the following key systems for smoother business operations:
- eCommerce Platform
- CRM
- Project Management
- Business Intelligence
- Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
- Enterprise Asset Management (EAM)
1. eCommerce – ERP Integration
When it comes to organization, data collection should always be associated with implementation. Most of the customer data or those that are external to the organization originates at the eCommerce store – the point where your business talks with its intended customers. Data such as leads, customers, orders, transactions and shipping stats arise at eCommerce.
Integrating your ERP with ecommerce store ensures that data is available to all members of the company who need to work on fulfilling a requirement that arises in the eCommerce store.
Most businesses implement their eCommerce stores on platforms such as Magento, Shopify, and SAP Hybris, where the quantum of the depth of information that’s generated in the front end is huge, so it will be an uphill task without integrating these platforms with your ERP tool.
Common Benefits Of eCommerce ERP Integration:
- Uniform availability of front-end data across departments
- Automatic update of inventory levels both in the front end (eCommerce) and back end (ERP)
- Dynamic pricing can be implemented, customer-specific and in real-time
- Easy to operate and execute in case of contingencies, such as the immediate requirement of the product that’s out of stock
2. CRM – ERP Integration
Any successful business is marked by superior customer service and satisfaction. CRM is a datahub for everything that’s related to customers, their transactions, orders, communications and much more.
A lot of times, salespeople are blamed for poor sales funnel performance, when in reality the other departments such as order management, logistics, and inventory teams function poorly.
This arises due to non-communication between your ERP software with the CRM application. That is why integration between ERP and CRM is crucial, mainly for creating a synergy between Demand (CRM) and Supply (ERP).
Common Benefits Of CRM ERP Integration:
- Teams can work collaboratively towards fulfilling a customer requirement
- Optimized sales funnel conversions and performance
- Quick effective customer service and consequential customer satisfaction
- Uniform customer information across systems and departments due to synchronized ERP CRM systems
Also read: How to Set up a Successful CRM-ERP Integration
3. Project Management – ERP Integration
Project Management is another indispensable activity for any organization, especially enterprise ones. It is what provides all information related to the project currently being worked upon, who works on what tasks, deadlines, and other activity related information.
Most ERPs provide an inbuilt project management solution, however, we recommend you to go for a stand-alone tool since it provides many more features and sophistication with respect to project management. And, integrating your project management tool with your ERP does wonder for not only the manager but also every employee.
Common Benefits Of Project Management Integration With ERP Software
- All department leads know the completed, on-going and scheduled works of employees
- Easy for work schedule in cases where a team can only start the process after another team completes
- Easy for employees of all hierarchies to prioritize tasks and consequent deadlines
4. Business Intelligence – ERP Integration
Business Intelligence software help take your organization to the next level. It facilitates by providing insights on various fronts that help make stakeholders decisions regarding new feature introduction, business diversification, new product launch, penetration of new markets, forecasts and targets for the upcoming financial year, and so on.
Though I have mentioned only high-level actionable insights here, one can leverage the tool to make any level of decision, even right down to the employee level, such as workflow changes facilitating efficient ergonomics, and so on.
By integrating your ERP application with BI software, you make sure employees across departments and hierarchies are able to access these actionable insights and make decisions within their degrees of freedom.
Common Benefits Of Business Intelligence Integration With ERP
- All employees are empowered by data and insights
- Everyone in the employee hierarchy can collaborate in providing organization-level suggestions that can create a breakthrough
- Accurate forecasting and consequently enhanced decision making
- Transparency, openness, and freedom to make decisions for all would mean elevated employee satisfaction
5. Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) – ERP Integration
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is a platform that facilitates electronic data transfers in a prescribed format across organizations such as trade partners, suppliers, distributors, and more.
Data such as purchase orders, transactions, shipment details, inventory levels need to be instantaneously communicated between organizations, as and when they sprout up and in a secure manner. That’s exactly what EDI serves to accomplish.
But where will the EDI get the data to be transferred? All the above-mentioned details arise either in eCommerce, ERP or PDT devices in offline stores. But since ERP is the primary source of truth for data, it goes without saying that your EDI application must be integrated with the ERP.
Common Benefits Of EDI ERP Integration
- Instant data transfer among business partners enabling seamless order management (NOTE: eCommerce must be Integrated with ERP for real-time data synchronization in order to achieve this)
- Accuracy in data communicated with respect to inventory, orders, invoices, shipping (and much more) improves, leading to faith in data received or sent.
- Ultimately improved supply chain and logistics for your eCommerce organization.
6. Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) – ERP Integration
Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) is a software that helps you to manage an organization’s assets such as raw materials, installation devices, vehicles, heavy equipment that ensure production. EAM is a must especially if you are in the manufacturing sector.
Even otherwise, EAM might streamline the way all your organization’s assets are managed. All activities such as managing inventory, supply chain, demand planning and forecasting, maintenance management that are related to handling companies’ assets.
These functionalities of an EAM can be optimized and made much more efficient by integrating enterprise systems with the ERP, thereby synchronizing inventory, logistics, human resource and other relevant data with the EAM system.
Common Benefits Of EAM ERP Integration
- Effective utilization of physical and financial assets for asset maintenance management by keeping the corresponding data points between two systems connected and synchronized.
- Advanced planning of human resources required for managing assets.
- Comprehensive planning of inventory requirements well in advance since the ERP Inventory data point is in sync with the EAM.
Related read: 10 Modern ERP Solutions for Manufacturers & Distributors
Common Challenges And Solutions In ERP Integration
While it is obvious that ERP Integration solves several business pain points as stated above, it does not seem to be a cakewalk. There exist a few major challenges that come with integrating your ERP with other business applications.
These challenges can be classified as pre-integration and post-integration challenges, and they need to be paid attention to before stepping in.
1. Data Issues
- Challenges: Disparate systems within an organization often lead to data silos, where information is isolated and inconsistent across departments. This fragmentation complicates the consolidation of data into a unified ERP system, making it difficult to maintain accuracy, completeness, and consistency. Poor data quality resulting from these silos can undermine the reliability of the ERP system, affecting decision-making and operational efficiency.
- Solution: Implement a data integration platform that connects disparate systems to create a unified data environment. Establish data governance policies that define standards for accuracy, cleanliness, and maintenance. Encourage cross-department collaboration to ensure seamless data flow and use data quality tools to cleanse and deduplicate information before it enters the ERP system. This approach helps break down silos and ensures high-quality data across the organization.
2. Complex Data Mappings
- Challenges: Mapping data fields from various sources to the ERP system can be complex and time-consuming, requiring a deep understanding of both the source and target data structures. This process is often a bottleneck in ERP integration projects.
- Solution: Simplify data mapping by using advanced ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools with user-friendly graphical interfaces. Engage data experts early in the project to define clear mapping rules and ensure accurate and efficient data transformation and integration.
3. Real-time Data Integration
- Challenges: Achieving real-time data integration across systems is difficult, especially when dealing with legacy systems that do not support real-time data exchange. This can result in delays and inaccuracies in data availability.
- Solution: Use integration platforms that support real-time or near-real-time data synchronization. Consider adopting a microservices architecture to facilitate faster and more flexible data exchanges, ensuring that data is always current across your ERP system.
4. Technical Expertise
- Challenges: A lack of in-house technical expertise can be a significant barrier to successful ERP data integration. The process requires deep knowledge of both the ERP system and the external data sources being integrated.
- Solution: Invest in training for your staff to build the necessary skills for data integration. Alternatively, partner with experienced vendors and consultants who can provide the expertise needed to ensure a smooth and successful integration process.
5. API Limitations
- Challenges: Working with APIs in ERP integration can be tricky. You might run into rate limits, which slow down data syncing, or find that certain ERP functions aren’t supported by the API, requiring manual workarounds. Additionally, keeping up with API updates and changes can be time-consuming and disrupt your operations if not managed properly.
- Solution: To tackle these issues, you can use batch processing to reduce API calls and schedule syncs during off-peak hours. For unsupported features, consider developing custom APIs or using middleware to fill in the gaps. Stay proactive by setting up monitoring systems for API changes and regularly updating your integration code to avoid disruptions.
6. Middleware Dependencies
- Challenges: Middleware can add complexity to your IT setup, requiring specialized management skills, and it can also be costly to implement and maintain. Moreover, relying heavily on a specific vendor can limit your flexibility and increase expenses as your business grows.
- Solution: Simplify by choosing well-supported middleware with comprehensive documentation. Keep costs under control by selecting scalable solutions and negotiating contracts to account for future growth. To avoid vendor lock-in, opt for middleware that supports open standards, and regularly assess your technology stack for alignment with your business needs.
7. Scalability And Performance Issues
- Challenges: As data volumes grow, your ERP system might struggle, leading to slower performance and dissatisfied users. Concurrent processes can cause delays, and limited computing resources might not be enough to handle the load, requiring ongoing system optimization.
- Solution: Invest in scalable infrastructure, such as cloud-based solutions, to handle larger data volumes. Implement load balancing and concurrency controls to maintain smooth operations. Regularly audit and optimize your resources and consider re-architecting parts of your system to improve efficiency.
8. Security And Compliance Concerns
- Challenges: Protecting sensitive data and ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA is crucial, but it can be complex and resource-intensive. Encrypting data, managing access controls, and maintaining compliance documentation add to the challenge.
- Solution: Strengthen security by implementing role-based access controls and keeping your encryption standards up to date. Use automated tools to manage compliance and maintain audit trails. Stay informed about regulatory changes and adjust your processes accordingly to ensure ongoing compliance.
9. Organizational Change Management
- Challenges: Introducing a new ERP system or updating existing components can face resistance from users accustomed to old workflows. This resistance can slow down adoption, making effective training and alignment with business goals essential but challenging.
- Solution: Create customized training programs tailored to different user groups and adopt an iterative learning approach to ease the transition. Engage users early and provide continuous support. Align the integration project with business goals through strategic planning and regular performance evaluations.
10. Cost And Resource Constraints
- Challenges: ERP integration projects often face budget overruns due to unforeseen technical issues, scope creep, and hidden costs like additional licenses or third-party tools. Limited internal resources and the need for specialized skills can also strain the project.
- Solution: Prevent budget overruns with detailed planning, strict scope management, and a contingency budget. Conduct a thorough cost analysis to uncover hidden expenses and ensure vendor transparency. Address resource constraints by strategically outsourcing and investing in staff training to build necessary expertise.
Successful ERP Integration Strategy Using DCKAP Integrator
By now, you know how quintessential ERP Integration is, the types of ERP Integration, the need, and benefits, as well as the challenges that need to be attended to while integrating your ERP software.
For example, DCKAP Integrator is a cloud ERP integration middleware that completely takes care of integrating your ERP with your business applications, and it automates your data transactions between applications. DCKAP Integrator also solves your custom integration requirements through an array of features such as custom flow builder, advanced mapping and modifiers, intuitive dashboards, error logs, and so on.
DCKAP Integrator has been providing seamless integration solutions for over 100 customers using leading ERP platforms like SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics, Epicor, NetSuite, Distribution One, DDI Inform, and much more. Whether your systems are in the cloud or on-premises, our team of integration experts can customize the solution to fit your business processes.
Schedule a free demo with an integration expert now!
FAQs
How is ERP Integration different from ERP implementation?
ERP implementaion comes first. It involves the process of setting up your ERP system. ERP Integration, on the other hand, involves ensuring bi-directional data-flow between the ERP and other applications, such as your ecommerce platform, CRM, PIM, marketplace, EDI and others.
What are the common use cases for ERP integration?
Common use cases for ERP integration include:
- Connecting ERP with ecommerce platforms to automate order processing and inventory updates.
- Integrating with supply chain management tools to optimize procurement and logistics.
- Linking with financial systems to improve budgeting, forecasting, and reporting.
- Connecting with CRM systems to enhance customer experience and relationship management.
- Synchronizing data across different systems to ensure consistency and accuracy in business operations.
What are the types of ERP integration?
There are several types of ERP integration, including:
- Point-to-Point Integration: Directly connecting two systems with custom code.
- Cloud-Based Integration: A modern approach where cloud-based tools enable seamless communication between ERP and other systems, making it ideal for small businesses with limited technical resources.
- Middleware Integration: Using an enterprise service bus (ESB) to facilitate communication between different systems.
- Application Programming Interface (API) Integration: Leveraging APIs to allow ERP systems to exchange data with different software applications.
What are the best practices for ERP integration?
The best practices for ERP integration include thoroughly planning to understand your business needs, ensuring data integrity with strong governance, using scalable solutions that can grow with your business, extensively testing the system to catch issues early, and continuously monitoring the integrated system to make necessary adjustments over time.
Why Should You Opt For ERP Integration?
Though it’s relevant that ERP as a whole is an integrated set of different data points of an organization, it needs to integrate with several business systems so that it can improve the overall accuracy of operations. First, let’s look at what could go wrong if you don’t have an integrated system in place for your business.
- Manual Effort Is Slowing You Down: Now imagine a lead form submitted through your eCommerce website. Without an integrated ERP system it remains in your eCommerce unless someone manually makes an entry into the ERP. This increases workforce burden and lessens operation effectiveness. ERP Integration is a must to eliminate this time consuming, labor-intensive work.
- Error-Prone Operations Is Getting Costly: This pain point arises as a consequence of the above-mentioned point with manual data entry. Humans are error-prone and tend to make mistakes. This leads to entering wrong or missing customer and product data into ERP systems, resulting in departments working with incorrect information and an avalanche of other problems, which ultimately ends in customer dissatisfaction and dropouts.
- Real-Time Data Unavailability: As seen in the above two points, disintegrated systems mean manual data updates. This implies that the data is not communicated with the ERP immediately, as and when it arises. Ultimately, the relevant stakeholders in your company only tend to their activities, thereby wasting valuable days by manually transferring data.
- Poor Sales Funnel Conversions: Sales Funnel is the end-to-end cycle from a person visiting a website, to a person doing business with a company, and ultimately even repeat business. This includes a lot of stages such as the lead, prospect, customer, repeat customer and business evangelist. An efficient sales funnel indicates higher conversion rates and reduced conversion times from one stage to another. This is an unlikely possibility without ERP System Integration, thereby handing your business a poor sales funnel and making you lose out on a chunk of leads that can become customers.
- Hampered Team Collaboration: Consistency of data between systems is imperative for different teams to work with the same objective and intensity and without conflicts. This means that without ERP System Integration, team collaboration is bound to be hampered, such as in this scenario of inventory management:
So You Have An iPaaS Now. What Next?
Integrating your ERP System with your business-critical applications is simple and straightforward. The usual steps to configure your ERP Integration with systems using a simple iPaaS like DCKAP Integrator are as follows:
- Add System Credentials: Firstly, you will need to configure the credentials (API token) for your ERP and other systems that you wish to integrate.
- Create Flows: Set up the base template for the interaction between your ERP and other applications as to when and how data should be transferred, and how CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations should be performed.
- Configure Integration Pipes: Pipes are nothing but data points in your systems, such as Customer Data, Product Data, Order Data, and so on. All you have to do is configure similar pipe connections (e.g. Inventory Data) in the connected systems (ERP and eCommerce).
- Set Up Mapping And Modifiers: Up next, set up connections between the data fields of ERP, eCommerce, and CRM systems. (e.g. “Customer Name” field from ERP split and mapped to “First Name” & “Last Name” fields of CRM.) Set up advanced business logic on how data fields should interact with each other. (e.g.: Split “Customer Name” in ERP into data fields “First Name” and “Last Name” of CRM).
- Enable Auto Mode: Make it so the integration between the ERP system and other applications goes live after automating and setting up the sync schedule and frequency (real-time synchronization, if needed). Your Integrator application will take charge from now on.
In this Story